
In conclusion Electron affinity is more difficult to analyse in molecules as their structure is shows complications. The elements Chlorine strongly attracts electrons while mercury is the element with atoms that most weakly attract an electron. Non-metals typically have higher value than metals. If value is positive the process is exothermic and occurs spontaneously.Įach of these elements has a completely filled valence electron shell and an electron affinity that approaches zero. The negative electron affinity of the surface, which results in the sharp peak at the low-energy end of the spectrum, has clearly been removed from the surface. The value may be either positive or negative value, the negative value means energy must be present in order to attach an electron to the ion, here the capture of electrons is an endothermic process. What is Electron Affinity Chemists define electron affinity as the change in energy, measured in units of kJ/mole, experienced when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. This corresponds to an exothermic process, a release of energy.

If the electron affinity is positive, and we can use the symbol E ea, the enthalpy change for the same process is negative. It increases when it moves down a column or group and also shows an increase when it moves from left to right across a period or row( except for the noble gases). The electron affinity is the release of the energy, that’s the amount of energy coming out, while the enthalpy change is the change in energy of the system. When the value of electron affinity is negative, we have exothermic electron affinity while when the value of electron affinity is positive, we have endothermic.
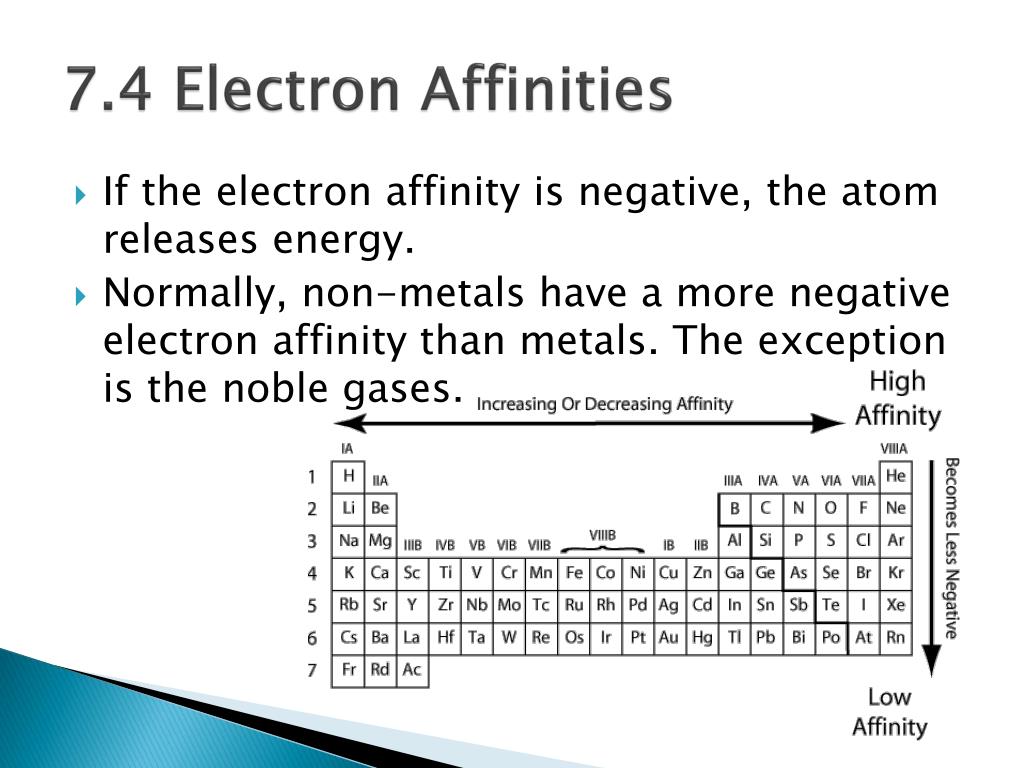

The noble gases will sometimes have negative electron affinities, indicating that it is an exothermic process to remove an electron from these elements. The halogens, again, have very high electron affinities. Electron affinity follows a particular path on the periodic table. In chemistry and atomic physics, the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as: the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom or molecule (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion. In contrast, electron affinity describes the energy change when an electron is added to an atom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
